Dr. Dostali Aliyev
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc is the displacement of the disc, which acts as a shock absorber between the vertebrae, towards the spinal canal or the part where the nerves exit, due to the gradual tearing of the protective layer around it. The prevalence of this disease in the community is around 70%.
Although it can occur at almost any age, it is more common in older age. Aging and degeneration, excessive weight, and sudden tension caused by lifting heavy loads can lead to a herniated disc.
Not every herniated disc is painful. In most patients who complain of pain, it is either back pain or radiating pain to the leg in case of nerve compression. Coughing or bending forward can increase the pain. Especially in minor herniations where pain is predominant, the edema caused by the hernia creates more pressure on the nerves.
Although herniated disc is highly prevalent in the community, only 2% of cases require surgical treatment.
Not every herniated disc requires surgery. If there is no loss of strength, decrease or loss of reflexes in the patient, surgery is not immediately recommended.
In cases where there is no indication for surgery and pain is predominant, the success rate of algological interventional procedures aimed at inflammation and edema in the herniated area is very high.
Algological interventional procedures are performed in the operating room, under sterile conditions, under local anesthesia, and with radiological imaging. After being observed for a few hours, the patient can go home on the same day.
Using a special needle under radiological imaging, the area where the nerve is compressed is reached, and after confirming that the needle is in the correct place without puncturing any blood vessels, a mixture of local anesthetic and steroid is injected.
In pulsed radiofrequency treatment, after confirming the location of the needle with signals given by the radiofrequency device, radiofrequency therapy is applied.
In addition, radiofrequency ablation treatment applied to the herniated disc with a special radiofrequency needle is also one of the successful algological interventional procedures.
As a result of these procedures, a decrease in inflammation caused by herniated disc, shrinkage in the size of the hernia, and relief of compressed nerves are observed. Significant reduction in the patient’s pain is seen after the procedure.
After algological interventional procedures, there are things that patients should always pay attention to. Among them, we can mention losing excess weight, quitting smoking, performing exercises to strengthen the back, spine, and abdominal muscles, and correcting inappropriate postures and sitting and lying positions.
Remember, preventing a herniated disc is easier than treating it.
Wishing you healthy days…
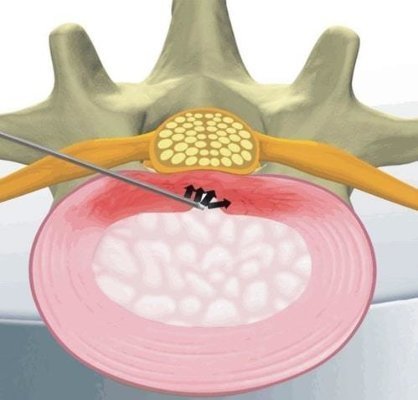
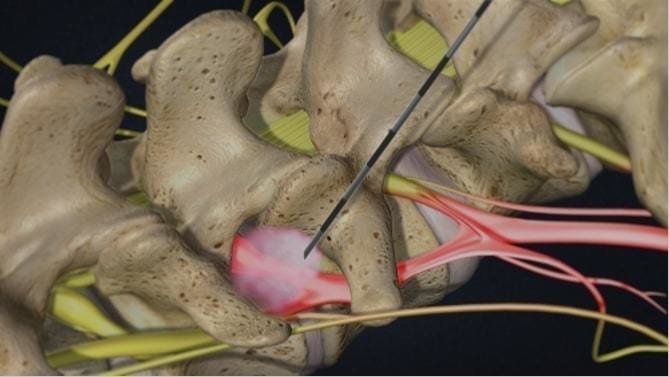
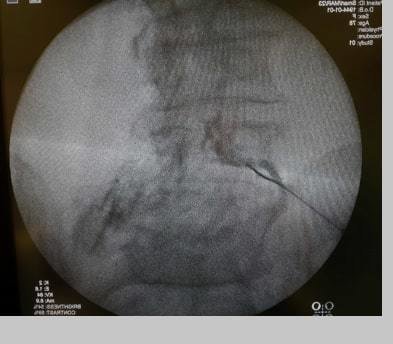
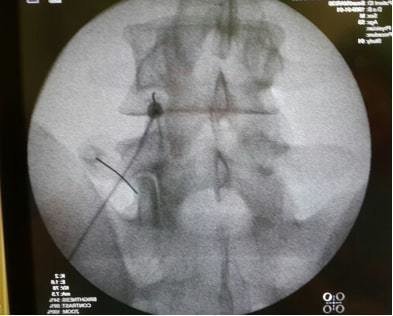
Figure 1. Intra-disc radiofrequency ablationFigure 2. Transforaminal steroid injectionFigure 3. Transforaminal steroid injectionFigure 4. Dorsal Root Ganglion RF
Specialist Dr. Dostali Aliyev
Herniated disc is the displacement of the disc, which acts as a shock absorber between the vertebrae, towards the spinal canal or the part where the nerves exit the spine due to the gradual tearing of the protective layer around it. The prevalence of this disease in the community is around 70%.
Although it can occur at almost any age, it is more common in advanced age. Aging and degeneration, excessive weight, and sudden tension caused by lifting heavy loads can lead to herniated disc.
Not every herniated disc is painful. In most patients who present with complaints of pain, back pain is observed, and in cases of nerve compression, pain radiating to the leg is observed. The pain may increase with coughing or bending forward. Especially in small herniations where pain is prominent, the edema caused by the herniation creates more pressure on the nerves.
Although herniated disc is highly prevalent in the community, only 2% of cases require surgical treatment.
The treatment of every herniated disc is not surgery. If there is no loss of strength, decrease or loss of reflexes in the patient, surgery is not immediately sought.
In cases where there is no indication for surgery and pain is predominant, the success rate of algological interventional procedures applied for inflammation and edema in the herniated area is very high.
Algological interventional procedures are performed in the operating room, under sterile conditions, under local anesthesia, and with the guidance of radiological imaging. After being observed for a few hours, the patient can go home on the same day.
With radiological imaging, a special needle is used to reach the nearest area where the nerve is compressed, and after confirming that the needle is in the correct position without any vascular puncture, a mixture of local anesthetic and steroid is injected.
In pulsed radiofrequency treatment, after confirming the location of the needle with warnings given by the radiofrequency device, radiofrequency treatment is applied.
In addition to these, radiofrequency ablation treatment applied to the hernia with a special radiofrequency needle is also one of the successful results of algological interventional procedures.
As a result of these procedures, a decrease in inflammation caused by herniated disc, shrinkage in the size of the herniation, and relief in the compressed nerves are observed. A significant reduction in the patient’s pain is seen at the end of the procedure.
After algological interventional procedures, there are always things that patients should pay attention to. Among them are; getting rid of excess weight, quitting smoking, performing exercises to strengthen the back, spine, and abdominal muscles, correcting inappropriate postures, sitting, and sleeping positions.
Remember, preventing herniated disc is easier than treating it.
Wishing you healthy days…
Figure 1. Intra-disc radiofrequency ablationFigure 2. Transforaminal steroid injectionFigure 3. Transforaminal steroid injectionFigure 4. Dorsal root ganglion rf