Heart vascular disease is still a leading cause of death and disabilities worldwide, including in our country. Heart vascular disease generally occurs due to the blockage of the vessels that nourish the heart, usually referred to as coronary arteries. The most common cause of these blockages is the accumulation of fatty plaques on the vessel wall, known as atherosclerosis, progressing over time and obstructing blood flow within the vessel. Fatty plaques sometimes harden by calcifying, forming more rigid and solid plaques. These calcified plaques can hinder the passage of materials such as balloons/stents used to open blockages, making it impossible. As a result, the balloon/stent cannot pass through the vessel blockage. Additionally, the use of inappropriate materials can lead to problems such as tearing and puncturing of the vessel, putting the patient’s life at risk.
Several new technologies have been introduced to open these rigid plaques. Two of these are the rotablator and lithotripsy. Both operate with different mechanisms. Sometimes one or both are used to open calcified narrowings, followed by the placement of a balloon/stent. Another benefit of these technologies is reducing the likelihood of stent blockage in the future. Of course, before new technological products are introduced, studies are conducted to demonstrate their safety and effectiveness, and then they are made available for commercial use.
Now, let’s provide brief information about these technological devices.
What is a Rotablator?
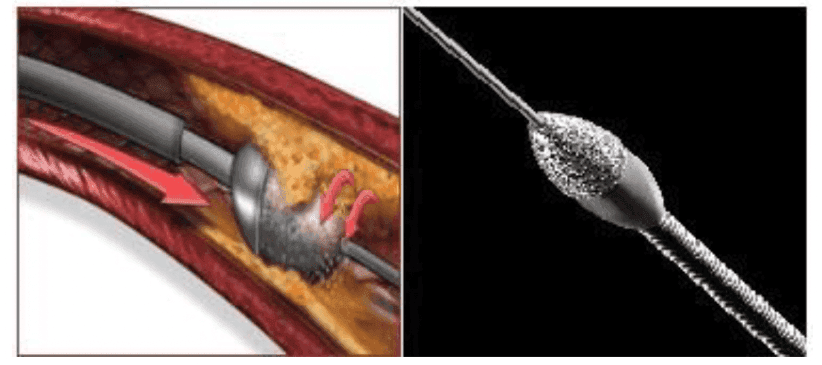
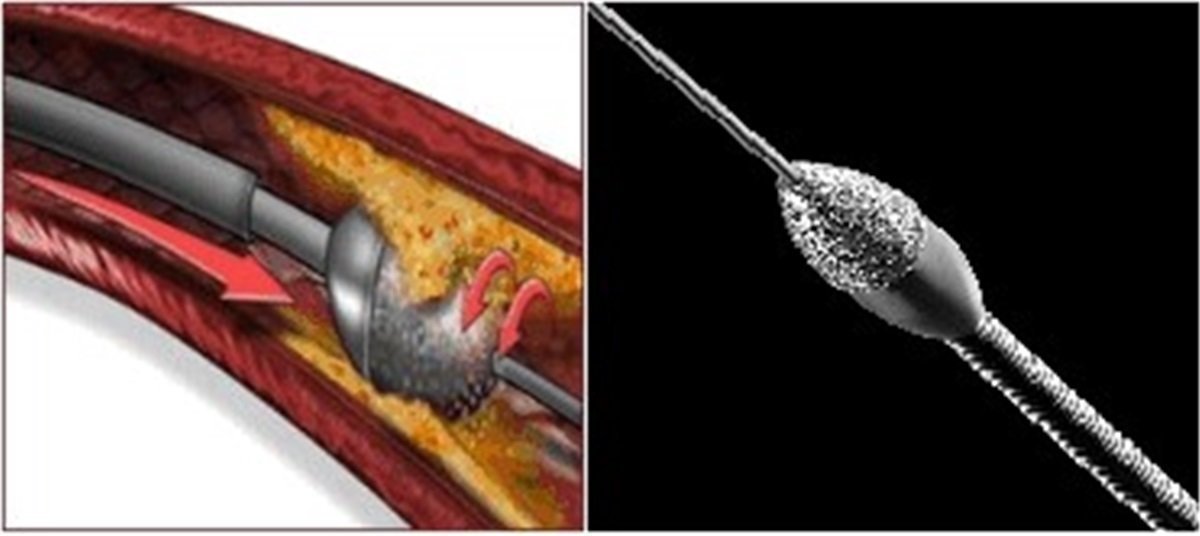
It is a small drill with a cutting blade at the end that rotates very rapidly to abrade the blockage. The sharp blade is specially coated with diamond dust. This diamond-coated head rotates very quickly on its axis (140,000-160,000 revolutions per minute), shaving off the calcified parts inside the blood vessel. The size of this diamond-coated device varies depending on the width of the vessel.
Image 1: The images above depict the rotablator device. In the colored image, the device is rotating on its own axis in the direction of the arrow. In the black and white image, the diamond-coated blade of the device is shown.
Procedure with Rotablator: Where and How is it Performed?
The procedure is performed in the angiography laboratory.
The procedure can be carried out through the groin or arm vessels. Plastic tubes (catheters) are inserted into your heart vessels through the sheaths placed in these vessels. Using these plastic tubes, the rotablator device is advanced to the specific narrowing. During and after the shaving process, the condition of the narrowing and any changes are examined through a normal angiography.
The procedure duration is at least 1 hour, but it varies depending on your vascular structure and the degree of calcification.
The procedure is not painful. Local anesthesia is applied when inserting the sheath through the groin or arm, as a needle is used. However, in some cases, chest pain may occur, and you should definitely inform your doctor about this during the procedure.
You can remain awake during the procedure. Additionally, depending on your preference or your doctor’s request, sedative drugs for relaxation can be administered.
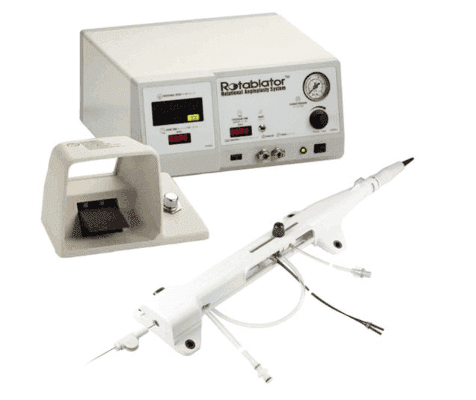
Image 2: In the image above, the connected diamond-coated blade of the device, the materials providing energy during the procedure, and the controlled other components are shown.
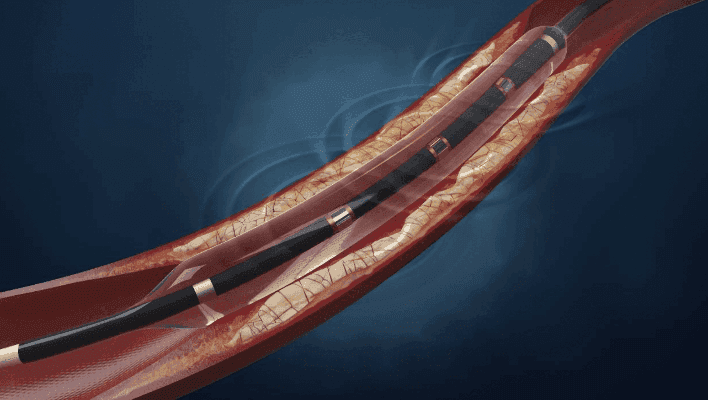
Lithotripsy: What is it?
It typically resembles the balloon system used to open blocked arteries. However, this balloon is a bit more special. It has a system at its end that generates and emits sound waves. The sound waves create pressure on the calcified plaque with a shock effect. The pressure created by the sound waves causes very small fractures in the calcified plaques. These small fractures allow the stent to be easily expanded and open effectively later.
The pressure created by the sound waves does not have harmful effects on tissues outside the hard calcified plaque.
Image 4: Circular sound waves are generated with a special balloon, and the shock pressures created by these waves spread to break the calcification in the vessel wall.